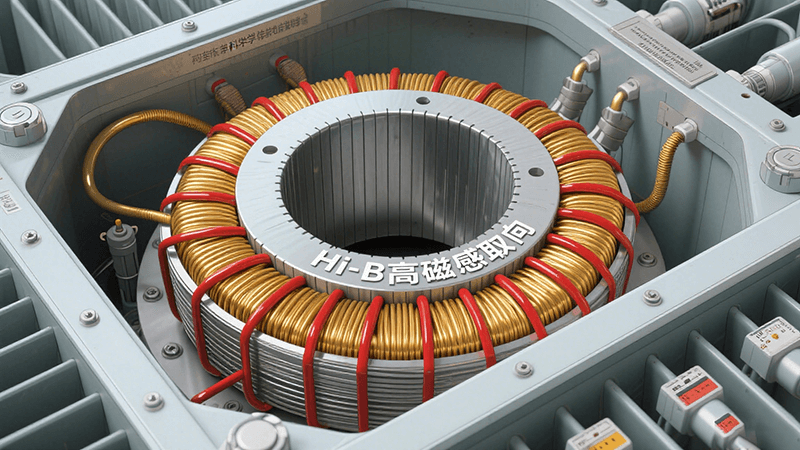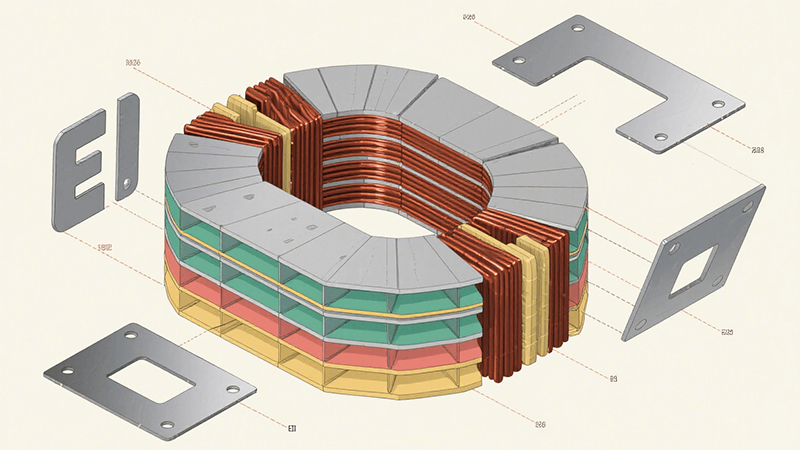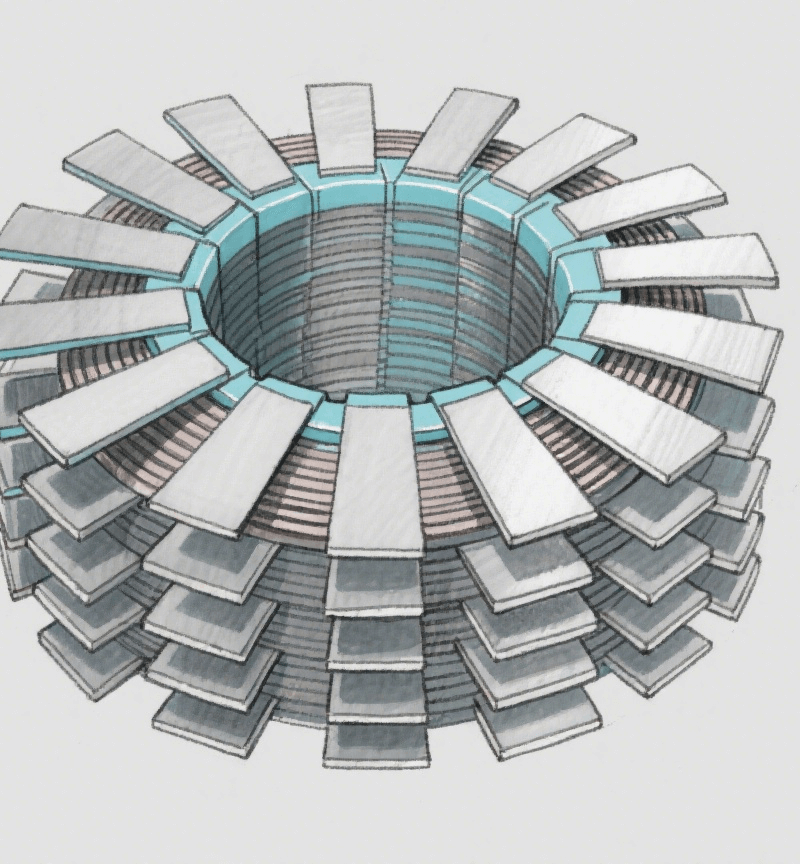
El núcleo de hierro trifásico de tipo EI: el pilar central y la evolución tecnológica en los sistemas eléctricos modernos
El núcleo de hierro trifásico tipo EI has a wide range of applications . In this era of rapid industrial advancement, stable power transmission has become a critical pillar supporting modern society’s operations. Within the complex system ensuring efficient power delivery from generation to end-users, transformers play an irreplaceable role.
As the core component of transformers, the performance of three-phase EI-type cores directly determines the equipment’s operational efficiency, stability, and service life. Companies with advanced technological expertise in transformer core manufacturing consistently emphasize that precisely selecting compatible materials and optimizing design solutions for demanding electrical scenarios is the fundamental prerequisite for ensuring equipment performance meets standards.
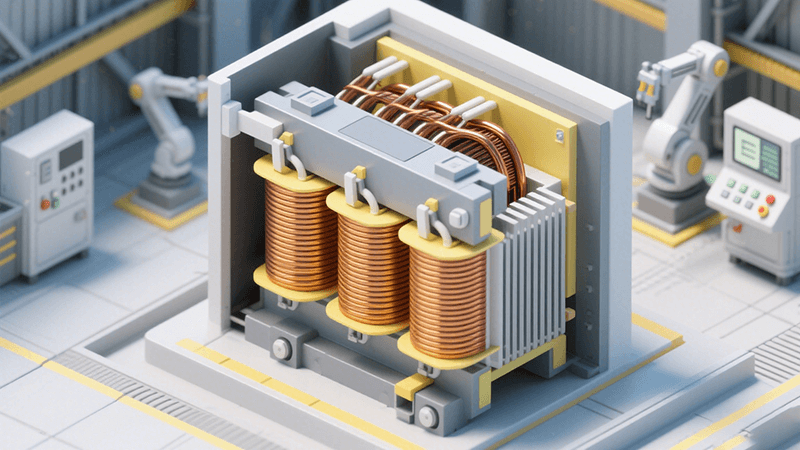
This article will delve into why three-phase EI cores have become a vital component in electrical engineering, elucidate their unique advantages, and outline their practical aplicaciones across various industries.
I. Foundational Understanding of Three-Phase EI Cores
Contenido
- 1 I. Foundational Understanding of Three-Phase EI Cores
- 2 II. Core Value of EI Structure in Electrical Engineering
- 3 III. Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Loss Control
- 4 IV. Diverse Applications of Three-Phase EI Cores
- 5 V. Durability Design and Mechanical Strength Assurance
- 6 VI. Innovative Evolution of Three-Phase EI Core Manufacturing Technology
- 7 VII. Comparative Analysis of EI-Type Cores vs. Other Core Designs
- 8 VIII. Positioning and Role of Professional Enterprises in the Global Market
- 9 IX. Future Outlook: Focusing on Sustainability and Technological Innovation
- 10 X. Conclusion: The Irreplaceability of Three-Phase EI Cores
The designation “three-phase EI core” originates from its distinctive structural configuration. It is fabricated by cutting high-grade silicon steel sheets into ‘E’-shaped and “I”-shaped cross-sections, which are then assembled through an alternating layering process. This layering technique minimizes internal air gaps within the core, effectively reducing energy losses and enhancing magnetic circuit utilization.
Compared to single-phase cores, the three-phase structure features an optimized magnetic circuit design that enables balanced distribution of electrical loads. Consequently, it finds extensive application in medium-to-large transformer equipment. Companies specializing in this field leverage high-precision silicon steel sheet cutting technology and stringent material selection standards to produce three-phase EI cores that deliver both operational stability and high efficiency, meeting the demanding requirements of real-world applications.
II. Core Value of EI Structure in Electrical Engineering
The significant advantage of the EI structure lies in its ability to ensure excellent magnetic efficiency while maintaining a simple and reliable mechanical structure. Compared to other core shapes, the core competitiveness of the three-phase EI core manifests in the following three aspects:
Manufacturing Convenience: Silicon steel laminations facilitate mass production, effectively controlling manufacturing costs and offering significant economic advantages;
Low Energy Consumption: The layered laminated structure substantially reduces eddy current generation, minimizing unnecessary current losses and heat accumulation;
Superior Magnetic Performance: The EI configuration ensures uniform magnetic flux distribution within the core, preventing performance degradation caused by localized excessive magnetic flux density.
Within specialized manufacturing facilities, engineers demand extreme precision in laminating silicon steel sheets—even minute stacking deviations can compromise the core’s overall performance. This rigorous control over accuracy ensures that three-phase EI cores maintain stable, reliable operation under high-load power conditions.
III. Enhancing Energy Efficiency and Loss Control
Minimizing energy loss is a core objective in transformer design, and the three-phase EI core plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. Transformer energy loss primarily stems from hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. Professional manufacturers effectively minimize these losses by utilizing high-permeability oriented silicon steel and precisely controlling the thickness of the laminations.
For industries pursuing energy conservation and consumption reduction, selecting structurally optimized EI core transformers represents not only a sound technical decision but also delivers significant economic benefits. Enhanced equipment operational efficiency directly reduces electricity consumption costs while supporting enterprises in achieving sustainable development goals.
IV. Diverse Applications of Three-Phase EI Cores
Three-phase EI cores demonstrate extensive application value across multiple industries due to their superior performance. Key application scenarios include:
Distribution Transformers: As critical components in power distribution, they ensure stable electricity supply to factories, office buildings, and residential areas.
Industrial Equipment: They provide precise voltage regulation for heavy machinery and production line equipment, guaranteeing stable operation.
Renewable Energy Sector: Performing vital power conversion and transmission functions in wind and photovoltaic systems, facilitating efficient grid integration of clean energy;
Automotive Electronics Sector: Delivering reliable power support for electric vehicle charging systems and onboard electrical equipment, meeting the technical demands of new energy vehicles.
To address differentiated needs across sectors, specialized manufacturers offer customized solutions. These involve adjusting core dimensions, optimizing material selection, and refining assembly processes to fulfill specific application requirements.
V. Durability Design and Mechanical Strength Assurance
During operation, transformers frequently encounter challenges such as load fluctuations and extreme environments (e.g., high temperatures, humidity, dust). The design of three-phase EI-type cores comprehensively addresses these demanding conditions. Manufacturers employ precise laminated silicon steel sheet stacking processes combined with advanced insulation techniques to ensure the core resists mechanical deformation under high-voltage conditions, possessing
V. Durability Design and Mechanical Strength Assurance
During operation, transformers frequently encounter multiple challenges such as load fluctuations and extreme environments (e.g., high temperatures, humidity, dust). The design of the three-phase EI-type core fully accounts for these demanding conditions. Through a precise laminated silicon steel sheet stacking process combined with advanced insulation treatment technology, the core maintains excellent structural stability and resists mechanical deformation under high-voltage conditions.
For transformers installed in complex environments like outdoor settings or industrial plants, core durability is particularly critical. Improper core design may lead to excessive vibration, localized overheating, or even equipment failure during operation. Rigorous quality control by specialized manufacturers ensures that three-phase EI cores maintain stable performance even under harsh operating conditions.
VI. Innovative Evolution of Three-Phase EI Core Manufacturing Technology
Advancements in materials science and automated production techniques have driven significant breakthroughs in three-phase EI core manufacturing. Today, high-permeability oriented silicon steel, laser precision cutting technology, and computer-aided design (CAD) have become mainstream production methods, propelling core manufacturing toward higher precision and efficiency.
Leading manufacturers leverage these advanced technologies to achieve strict control over silicon steel sheet thickness and core assembly alignment. This not only further enhances core operational efficiency but also effectively extends the overall service life of transformers. Additionally, the application of environmentally friendly coating technologies significantly boosts the core’s corrosion resistance, ensuring decades of stable equipment operation.
VII. Comparative Analysis of EI-Type Cores vs. Other Core Designs
Despite the widespread adoption of three-phase EI-type cores, alternative designs such as toroidal cores and C-type cores remain prevalent in the industry. While each core type offers distinct advantages, EI-type cores maintain high market penetration primarily due to:
Cost Advantage: Compared to toroidal cores, EI-type cores feature simpler manufacturing processes and lower mass production costs;
Standardization: EI laminations feature a comprehensive standardized size system, ensuring superior adaptability;
Maintenance Ease: During equipment maintenance or component replacement, EI cores facilitate quicker assembly and disassembly, reducing maintenance complexity and costs.
Specialized manufacturers consistently recognize that three-phase EI cores achieve an outstanding balance between performance, economy, and reliability, making them the preferred solution for most power applications.
VIII. Positioning and Role of Professional Enterprises in the Global Market
Amid growing global demand for reliable energy infrastructure, enterprises with technical advantages in transformer core manufacturing are actively expanding into international markets, supplying high-quality three-phase EI cores to customers worldwide. Through increased R&D investment, stringent manufacturing precision control, and optimized customer service systems, these companies have progressively established themselves as trusted suppliers within the transformer industry.
With exports to multiple countries and regions, coupled with deep collaborations with leading international power enterprises, these companies’ three-phase EI cores have achieved international performance and safety certifications, establishing a strong brand reputation in the global power market.
IX. Future Outlook: Focusing on Sustainability and Technological Innovation
Currently, the global energy system is accelerating its transition toward renewable energy, while smart grid development continues to advance. This trend is driving continuous innovation in transformer technology. As the core component of transformers, three-phase EI cores will continue to play a pivotal role in power systems. Their technological development will focus on two key directions: first, further enhancing material performance and optimizing magnetic circuit design; second, advancing production processes toward green and environmentally friendly upgrades to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions during manufacturing.
Leading enterprises have invested substantial resources in R&D, dedicated to developing cores with lower carbon footprints, exploring applications of recyclable materials, and enhancing core efficiency through technological innovation to align with global sustainability goals. It is foreseeable that as the energy sector transitions toward cleaner and more efficient practices, the EI-type core will remain the core component ensuring reliable power transmission.
X. Conclusion: The Irreplaceability of Three-Phase EI Cores
Three-phase EI cores are far more than simple laminated silicon steel components; they form the foundational backbone of efficient power transmission. Their critical role in reducing energy losses, enhancing equipment durability, and adapting to diverse industrial applications makes them indispensable in modern power systems. Through precision engineering and continuous technological innovation, specialized enterprises are driving performance upgrades in EI cores, ensuring they will continue to lead the direction of power transmission technology for decades to come.
For industrial enterprises, energy suppliers, and electrical engineers, selecting transformers equipped with high-quality three-phase EI cores represents not only a technical choice but also a strategic investment in equipment efficiency, operational reliability, and long-term sustainable development.